Before there were refrigerators folks kept drinks cool by putting them into clay jars that had been soaked in water. The evaporation of the water from the clay cooled the container and its contents, which today includes wine bottles. On the other hand, for many years artisans have taken clay in a slightly different form, shaped it and baked it and provided the teacups which keep the liquid inside until we drink it.
Two different forms of the same basic geological material, with two different behaviors and uses. Why bring this up? Well there is a growing series of articles which continue to laud the volumes of oil and natural gas that the world can expect from the artificial fracturing of the layers of shale in which these hydrocarbons have been trapped for the past few million years. It has been suggested that there is no difference between this “unconventional” oil and the “conventional” oil that has been produced over the past century to power the global economy. And yet, despite the scientific detail which some of these critics discuss other issues, they seem unable to grasp the relatively simple geologic and temporal facts that make the reserves in such locations as the Marcellus Shale of Pennsylvania and the Bakken of North Dakota both unconventional and temporally transient. Let me therefore try again to explain why, despite the fact that the oil itself may be relatively similar, the recovery and economics of that oil are quite different from those involved in extracting conventional deposits.
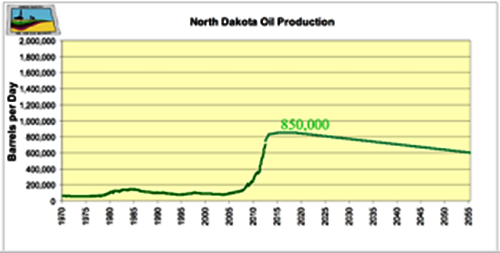
But, before getting to that, let’s first look at the current situation in North Dakota, using the information from the Department of Mineral Resources (DMR). According to theJanuary Director’s Cut the rig count in the state has varied from 188 in October, through 186 in November, and 184 in December, to 181 at the time of the report. Why is this number important? Well, as I will explain in more detail later, the decline rate of an individual well in the region is very high, and thus the industry has to continue to drill wells at a rapid rate, just to replace the decline. (This is the “Red Queen” scenario that Rune Likvern has explained so well.) The DMR recognize this by showing the effect of several different scenarios as the number of rigs changes.
For example they project that 170 rigs will be able to drill around 2,000 wells a year. At that level, and with some assumptions about the productivity of individual wells that I am not going to address here, but which Rune discussed. I would, however, suggest that it is irrational to expect that new wells will continue to sustain existing first year levels as the wells move away from formation sweet spots. Yet, accepting their assumptions for now, DMR project that the 170 rigs will generate the following production from the state:

……read more HERE












